Deno 1.30: Built-in Node modules
Deno 1.30 has been tagged and released with the following new features and changes:
- Support for built-in Node.js modules
deno.jsonbecomes an import map- Changes to
DenoAPIs deno fmtsupports configuring semicolons
📝 Help improve Deno and be entered for the chance to win a $100 Amazon giftcard by taking our survey.
If you already have Deno installed, you can upgrade to 1.30 by running:
deno upgradeIf you are installing Deno for the first time:
# MacOS and Linux
curl -fsSL https://deno.land/x/install/install.sh | sh
# Windows
iwr https://deno.land/x/install/install.ps1 -useb | iexClick here for more installation options.
Support for built-in Node.js modules
In Deno, npm packages have already had access to built-in Node.js modules such as fs, path, process, and many more through Deno’s Node.js compatibility layer.
In this release, these modules are exposed to Deno code via
node: specifiers.
import { readFileSync } from "node:fs";
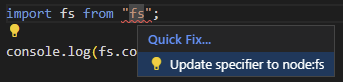
console.log(readFileSync("deno.json", { encoding: "utf8" }));Take note that importing via a bare specifier (ex.
import { readFileSync } from "fs";) without an import map is not supported. If
you attempt to do so and the bare specifier matches a Node.js built-in module
not found in an import map, Deno will provide a helpful error message asking if
you meant to import with the node: prefix. Additionally the LSP provides a
quick fix to update to a node: specifier.
If you are using code both with Deno and Node.js, the node: scheme will work
in both runtimes and it’s recommended to update to them for your Node.js code
anyway.
deno.json becomes an import map
This release brings a major update to the configuration file - it is now
possible to directly use a deno.json file as an import map. In previous
releases it was possible to tell Deno where to look for an import map file, by
specifying importMap key with a path to the import map file. Many users found
it useful, however this approach meant that there are two files with
configuration. To make it more concise you can now specify imports and
scopes keys in your configuration file and Deno will automatically start
treating the configuration file as an import map.
Example deno.json:
{
"imports": {
"std/": "https://deno.land/[email protected]/"
}
}Then the following script with a std bare specifier works:
import { assertEquals } from "std/testing/assert.ts";
assertEquals(1, 2);Can you see where we’re going with this?
Node/npm and LSP fixes
This release includes over 25 bug fixes related to the npm functionality and Node-API. Additionally, the LSP continues to be improved with over 10 bug fixes. See Releases for a full list.
Changes to Deno APIs
Changes to stable APIs:
Deno.permissionsAPIs get synchronous counter-parts:Deno.permissions.querySync({ name: "read", path: "./log.txt" }); Deno.permissions.revokeSync({ name: "read", path: "./log.txt" }); Deno.permissions.requestSync({ name: "read", path: "./log.txt" });
Thanks to Asher Gomez for implementing this feature.
Deno.writeFile()andDeno.writeTextFile()now accept aReadableStreamfor the second parameter.const stream = new ReadableStream({ pull(controller) { controller.enqueue(new Uint8Array([1])); controller.enqueue(new Uint8Array([2])); controller.close(); }, }); await Deno.writeFile("/tmp/test.txt", stream); assertEquals(Deno.readFileSync(filename), new Uint8Array([1, 2]));
A new
Deno.env.has(name)API was added:Deno.env.set("TEST_VAR", "A"); assert(Deno.env.has("TEST_VAR")); Deno.env.delete("TEST_VAR"); assert(!Deno.env.has("TEST_VAR"));
Deno.SeekerAPI gets support forbigintoffsets.You can now use the
biginttype as an argument to theSeekerinterface:const file = await Deno.open("./log.txt"); const cursor = await file.seek(150n, Deno.SeekMode.Start);
Test steps can be functions:
Previously, using the test steps API required the first argument of the test step to be a name or test definition:
Deno.test("my test", async (t) => { const success = await t.step("step1", async () => { await t.step(function inner1() {}); await t.step(function inner1() {}); }); if (!success) throw new Error("Expected the step to return true."); });
Starting with this release, the first argument can also be a named function:
Deno.test("my test", async (t) => { const success = await t.step(async function step1() { await t.step(function inner1() {}); await t.step(function inner1() {}); }); if (!success) throw new Error("Expected the step to return true."); });
API stabilizations:
Deno.Listener.ref() and Deno.Listener.unref() are now stable. The
--unstable flag is no longer required to use these APIs.
Changes to unstable APIs:
In
new Deno.Command({}).spawn(), the default value for thestdinoption was changed to"inherit"- meaning that if you don’t configure this option specifically, standard input will be inherited from the parent process.Deno.dlopenadds support for passing structs by value:const Rect = ["f64", "f64", "f64", "f64"]; const dylib = Deno.dlopen("./dylib.so", { make_rect: { parameters: ["f64", "f64", "f64", "f64"], result: { struct: Rect }, }, }); const rect_sync = dylib.symbols.make_rect(10, 20, 100, 200); assertInstanceOf(rect_sync, Uint8Array); assertEquals(rect_sync.length, 4 * 8); assertEquals(Array.from(new Float64Array(rect_sync.buffer)), [ 10, 20, 100, 200, ]);
Thank you to @DjDeveloperr and Aapo Alasuutari for implementing this feature.
New unstable APIs:
This release adds 3 new APIs:
Deno.osUptime()(requires--allow-sys=osUptimepermission)Deno.Conn.ref()Deno.Conn.unref()
These APIs require the --unstable flag, but we plan to stabilize them in the
next release.
Thank you to Kamil Ogórek for implementing this feature.
Removal of internal Deno.core
This release removes the Deno.core namespace. Deno.core was a private API
with no stability guarantees. This change should have no impact to the majority
of users.
deno fmt supports configuring semicolons
A long repeatedly requested feature for deno fmt has been the ability to
format without semicolons. It’s now possible to do this by using the
--options-no-semicolons flag or by specifying "semiColons": false in the fmt
configuration in a Deno configuration file:
{
"fmt": {
"options": {
"semiColons": false
}
}
}📝 Help improve Deno and be entered for the chance to win a $100 Amazon giftcard by taking our survey.

